As the world shifts toward sustainable energy solutions, solar lights have become a cornerstone of eco-friendly lighting for homes, gardens, and public spaces. At the heart of these systems are rechargeable batteries, which store solar energy to power illumination at night. Unlike disposable batteries, rechargeable batteries reduce waste, lower carbon footprint, and promote green living. This article explores the environmental benefits of using rechargeable batteries in solar-powered lighting, compares eco-friendly battery types like NiMH batteries versus NiCd batteries, highlights sustainable options like Bitpott, and provides practical battery recycling tips to minimize environmental impact.
The Environmental Case for Rechargeable Batteries
Solar lights are a beacon of sustainability, harnessing renewable energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. However, their environmental impact depends heavily on the batteries used. Disposable alkaline batteries contribute to electronic waste, with millions ending up in landfills annually, where they can leak harmful chemicals like mercury or cadmium. Rechargeable batteries, particularly NiMH batteries, offer a greener alternative by supporting hundreds to thousands of recharge cycles, significantly reducing waste. For example, a single rechargeable AA battery can replace up to 1000 disposable batteries, saving resources and reducing landfill contributions.
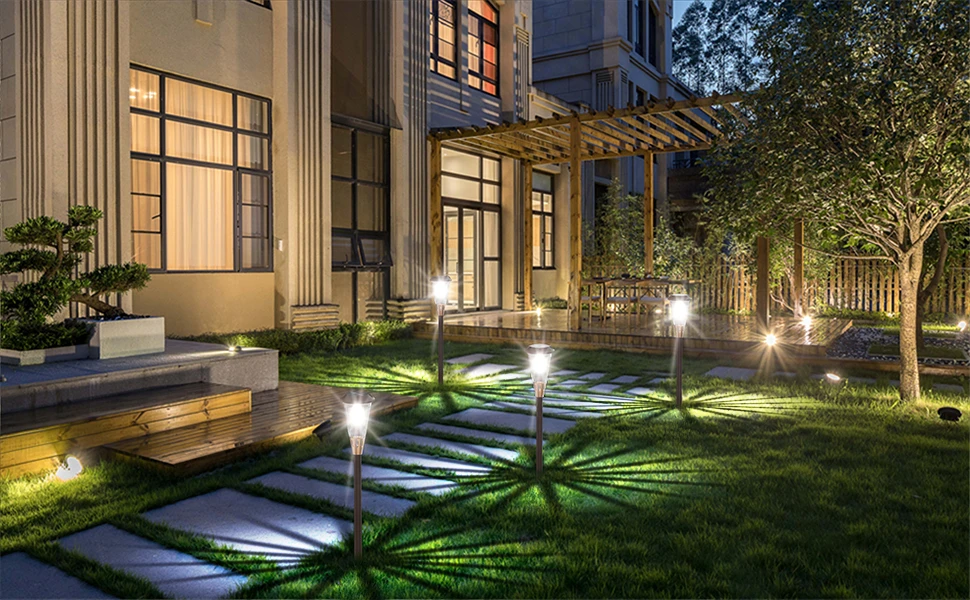

Beyond waste reduction, rechargeable batteries lower your carbon footprint. Producing disposable batteries requires energy-intensive mining and manufacturing processes. In contrast, rechargeable batteries for solar lights amortize their environmental cost over many cycles, making them a cornerstone of sustainable lighting solutions. By pairing solar-powered lighting with eco-friendly batteries, consumers can create a fully sustainable lighting system.
Comparing Eco-Friendly Battery Types for Solar Lights
Not all rechargeable batteries are equally sustainable. The two most common types for solar lights are Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) and Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) batteries. Here’s how they compare in terms of environmental impact:
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
- Environmental Advantage: NiMH batteries are less toxic than NiCd batteries, containing no cadmium, a heavy metal harmful to ecosystems and human health. They are safer for disposal and recycling.
- Performance: With capacities ranging from 600-2800 mAh, NiMH batteries suit various solar lights, from low-drain solar garden lights to high-power floodlights. They offer up to 2100 recharge cycles, enhancing longevity.
- Drawbacks: Slightly higher upfront cost than NiCd batteries, though their eco-friendly profile and performance justify the investment.
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
- Environmental Concerns: NiCd batteries contain cadmium, a toxic substance that poses risks if improperly disposed of. Regulations in many countries restrict their use due to environmental hazards.
- Performance: They have decent recharge cycles (around 1000) and perform well in extreme temperatures, but their capacity (typically 600-1000 mAh) is lower than modern NiMH batteries.
- Drawbacks: Due to their toxicity, NiCd batteries are being phased out in favor of NiMH batteries for solar-powered lighting.
Recommendation: For eco-friendly lighting, NiMH batteries are the clear choice due to their lower toxicity, higher capacity, and longer lifespan. Brands like Panasonic Eneloop, Tenergy, and Bitpott offer NiMH batteries optimized for solar lights.
Bitpott: A Sustainable Choice for Solar Lights
Bitpott’s AA NiMH batteries stand out as a sustainable battery option for budget-conscious, eco-minded consumers. With a capacity of 1100 mAh and up to 1000 recharge cycles, Bitpott batteries deliver reliable performance for solar garden lights and other low- to medium-drain applications. Their affordability (around $0.80-$1.20 per battery in bulk) makes them accessible for large-scale solar-powered lighting projects, such as illuminating community gardens or pathways.
Environmentally, Bitpott batteries align with green living by using NiMH technology, which avoids toxic cadmium. Their production emphasizes energy-efficient processes, reducing the carbon footprint compared to disposable batteries. While they offer fewer recharge cycles than premium brands like Eneloop (2100 cycles), their lower cost and decent performance make them a practical choice for sustainable lighting solutions.
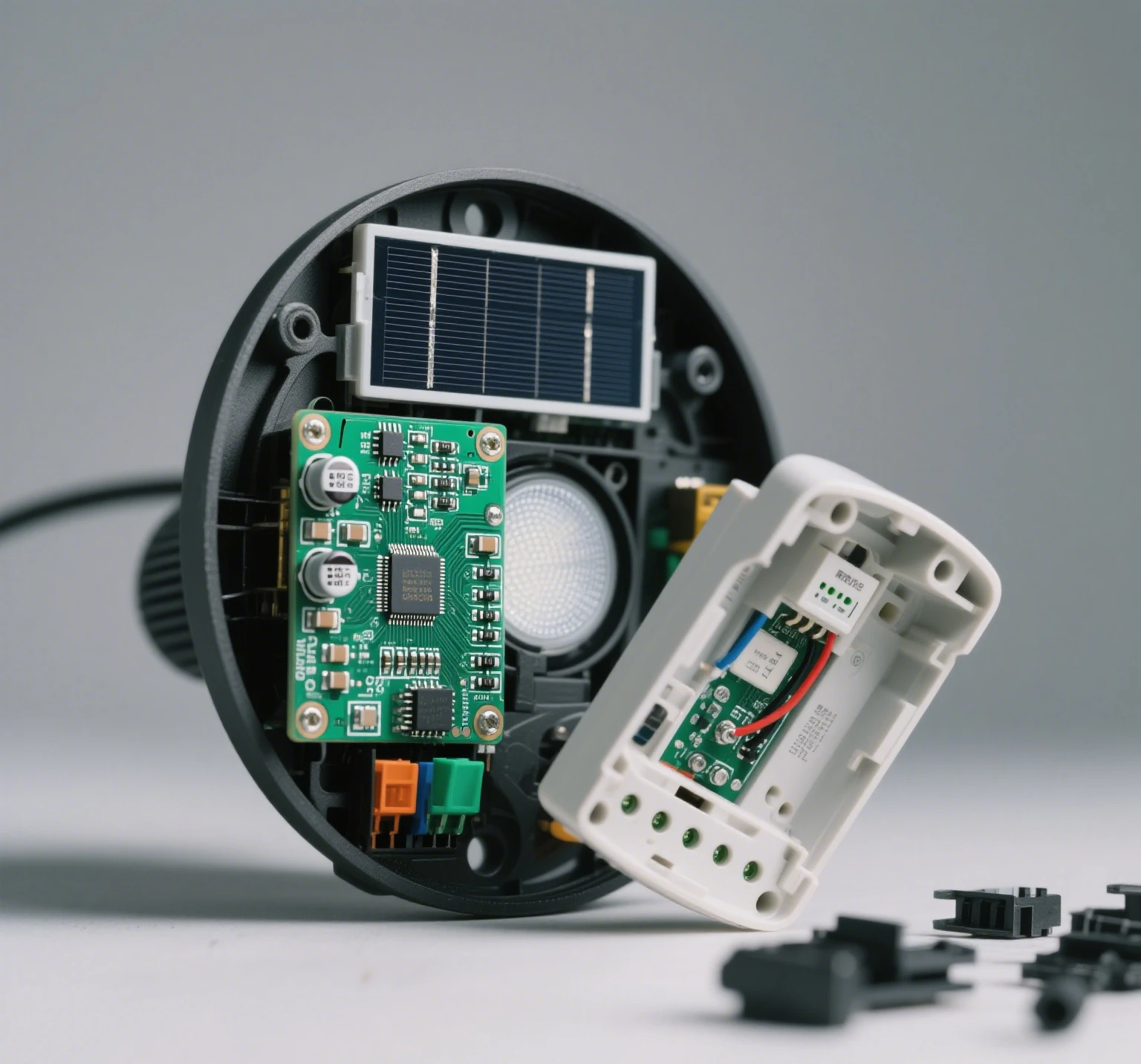
Environmental Impact of Rechargeable Batteries
Using rechargeable batteries in solar lights has far-reaching environmental benefits:
- Reduced Electronic Waste: A single rechargeable AA battery can replace hundreds of disposables, cutting down on the 3 billion batteries discarded annually in the U.S. alone, according to EPA estimates.
- Lower Carbon Emissions: The energy saved from fewer battery replacements translates to a reduced carbon footprint. For instance, over 1000 cycles, a NiMH battery can save the equivalent of 50-100 kg of CO2 compared to alkaline batteries.
- Resource Conservation: Rechargeable batteries require less frequent mining of raw materials like zinc and manganese, preserving natural resources.
However, the environmental benefits depend on proper use and disposal. Mismanaged rechargeable batteries can still harm the environment if not recycled correctly, underscoring the importance of battery recycling.
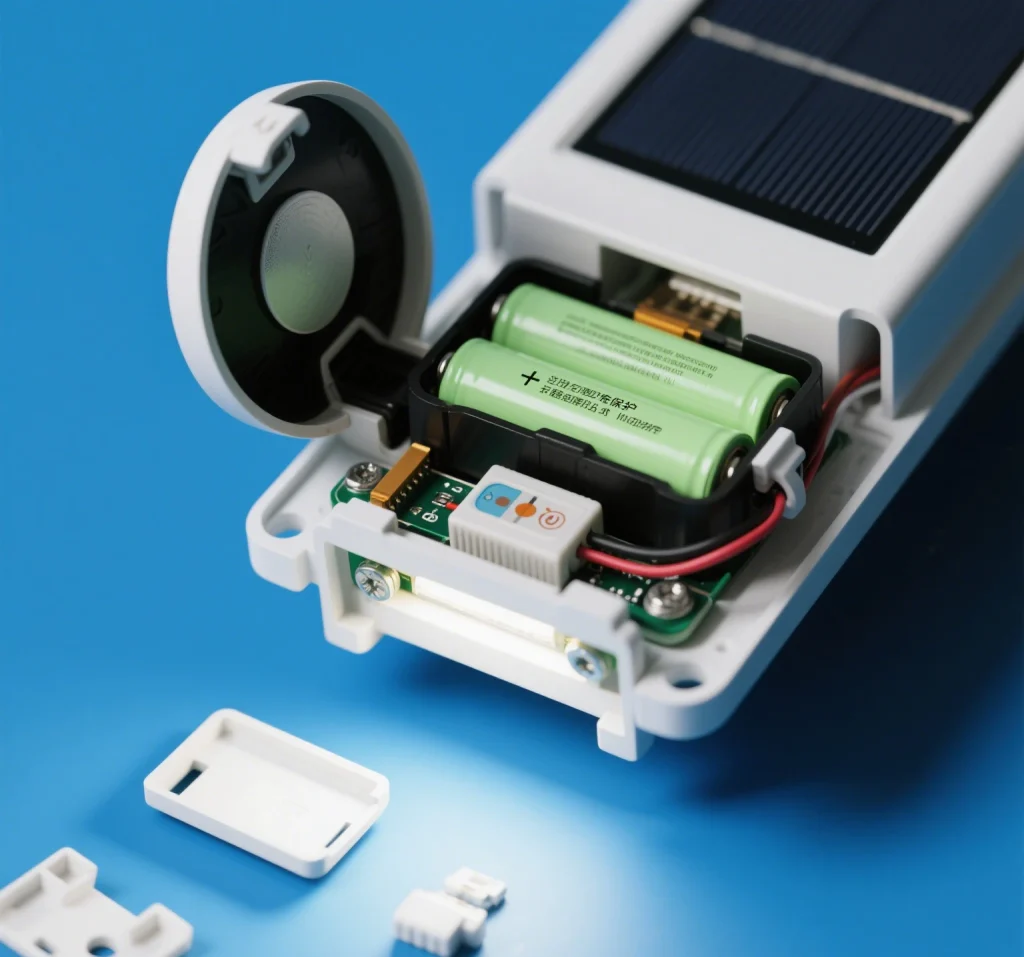

Practical Tips for Battery Recycling and Maintenance
To maximize the environmental benefits of rechargeable batteries for solar lights, follow these battery recycling tips and maintenance practices:
- Locate Recycling Programs: Many retailers, such as Home Depot or Best Buy, offer battery recycling drop-off points for NiMH batteries. Organizations like Call2Recycle provide free recycling services in the U.S. and Canada. Check local regulations for electronic waste disposal guidelines.
- Avoid Landfill Disposal: Never throw rechargeable batteries in household trash, as they may contain trace heavy metals that can leach into soil and water. Use designated battery recycling facilities to ensure safe processing.
- Extend Battery Life: To reduce replacement frequency, store rechargeable batteries in a cool, dry place to minimize self-discharge. For NiMH batteries, cycle them (charge and discharge) every 3-6 months to maintain capacity.
- Use Smart Chargers: Invest in a smart charger that prevents overcharging, which can degrade recharge cycles. Chargers like the Panasonic BQ-CC55 are optimized for NiMH batteries, enhancing their lifespan.
- Choose Low Self-Discharge Batteries: Batteries with low self-discharge, like Eneloop or Bitpott, retain charge longer when not in use, reducing energy waste in solar garden lights during cloudy periods.
- Monitor Battery Health: Replace batteries showing signs of wear, such as reduced runtime in solar lights, to maintain efficiency. Most NiMH batteries last 3-5 years with proper care.
By following these practices, you can ensure your rechargeable batteries contribute to eco-friendly lighting while minimizing environmental harm.
Comparative Analysis: NiMH vs. NiCd for Solar Lights
| Battery Type | Toxicity | Capacity (mAh) | Recharge Cycles | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiMH | Low | 600-2800 | 1000-2100 | Eco-friendly lighting, versatile use |
| NiCd | High (cadmium) | 600-1000 | ~1000 | Limited use, phasing out |
Key Takeaway: NiMH batteries are the superior choice for solar-powered lighting due to their lower toxicity, higher capacity, and alignment with green living goals.
Why Sustainable Batteries Matter for Green Living
The shift to rechargeable batteries in solar lights is more than a cost-saving measure; it’s a commitment to sustainable lighting solutions. By reducing electronic waste, lowering carbon footprint, and supporting renewable energy, NiMH batteries empower consumers to make environmentally responsible choices. Bitpott, for example, offers an affordable entry point into eco-friendly batteries, enabling widespread adoption of solar-powered lighting without compromising sustainability.
For green living enthusiasts, the impact extends beyond personal use. Communities adopting solar lights with rechargeable batteries can reduce municipal waste and energy costs. For instance, a neighborhood with 100 solar garden lights using NiMH batteries could prevent thousands of disposable batteries from entering landfills over a decade.
Conclusion: Powering a Greener Future
Rechargeable batteries are the backbone of eco-friendly lighting, enabling solar lights to deliver sustainable illumination with minimal environmental impact. NiMH batteries, like those from Bitpott, Panasonic Eneloop, and Tenergy, offer a non-toxic, high-performance alternative to NiCd batteries and disposables, reducing electronic waste and carbon footprint. By choosing sustainable battery options and following battery recycling tips, you can enhance the environmental benefits of solar-powered lighting. Embrace rechargeable batteries today to power your solar lights and contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.





Leave a Reply